Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) emerges from the processing of adipose tissue and represents a cutting-edge method within stem cell therapy, offering treatment options for a variety of autoimmune, neurological, urological, pulmonary, ophthalmological, and orthopedic conditions. SVF is a rich mixture of diverse stem cell populations, growth factors, and other vital biological elements. The extraction of SVF cells from adipose tissue is straightforward, with the entire procedure, encompassing anesthesia, extraction, and cell injection, consummated in approximately four hours in an outpatient setting. This treatment is generally well-received by patients and has been validated for safety in clinical settings.
Understanding SVF
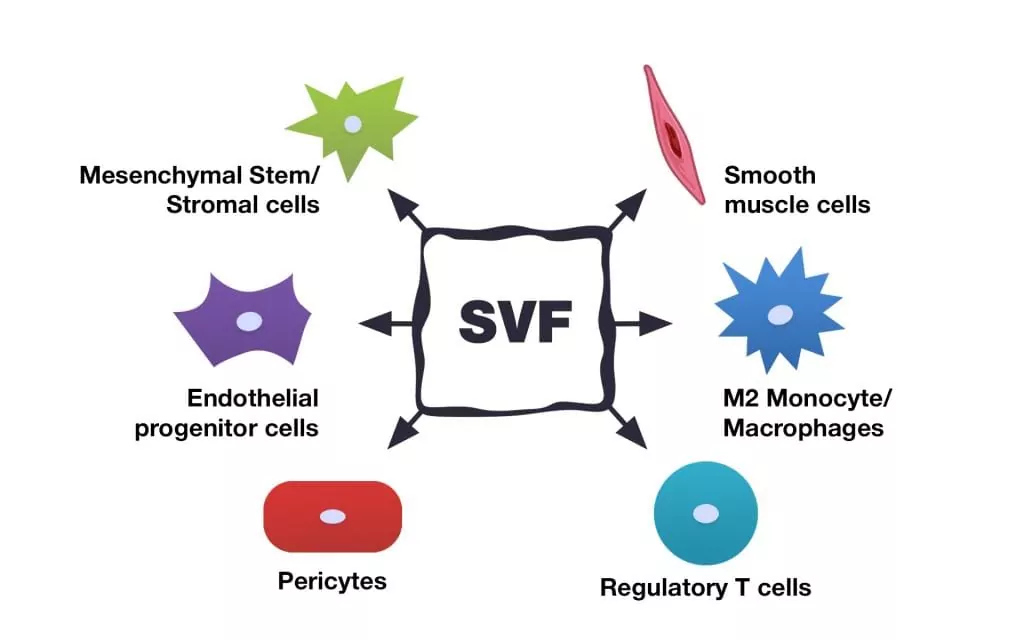
The Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) is derived alongside fat cells during adipose tissue processing. SVF is composed of a spectrum of stem cell varieties that are the forerunners to adipose cells, including immune cells, fibroblasts, pericytes, and endothelial cells, among others. Accompanied by growth factors and active biological substances, SVF has quickly become a focus for specialists exploring stem cell therapies due to its therapeutic promise. The procedure to isolate SVF cells is relatively uncomplicated, taking about 30–90 minutes using conventional liposuction techniques, and is completed within a few hours at a clinic. These stem cells can then be administered directly to the affected regions using a minimally invasive method.
The stromal vascular fraction (SVF) is composed of various cell subsets (adapted from the initial source). Within the SVF are diverse types of stem cells, including multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (multipotent MSCs), pericytes, and supra-adventitial cells. Additionally, it encompasses both progenitor cells, which have the potential to evolve into blood vessel wall cells, adipocytes, among other types, and mature cell types such as fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and adipocytes. The SVF is also rich in growth factors and a range of other active biological elements.
Individuals Who May Experience Positive Outcomes from SVF Therapy
The stromal vascular fraction (SVF) derived from adipose tissue shows significant therapeutic potential for managing prevalent ailments and medical conditions, including:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Joint degeneration
- Osteoarthritis
- Conditions affecting the Spine
- Injuries to soft tissues
- Damage to ligaments
- Migraines and tension-related headaches
- Diabetes
- Chronic ischemic heart disease
- Alopecia
- Erectile dysfunction
- Respiratory illnesses
- Various autoimmune disorders (such as multiple sclerosis, lupus, and Crohn’s disease)
Additionally, SVF therapy holds promise for neurological disorders like neuropathy, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Parkinson’s disease. Currently, numerous potential uses for adipose-derived stem cells are under clinical scrutiny.
How does SVF work?

Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF) is a component derived from adipose (fat) tissue. It's a complex mixture that includes a variety of cells such as adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), endothelial precursor cells, macrophages, fibroblasts, and other cell types. When applied to damaged or diseased tissues, the diverse cell types in SVF can contribute to healing and regeneration through several mechanisms:
1. Cytokine Secretion: The cells within SVF release cytokines and growth factors that reduce inflammation, diminish scar tissue formation, and promote tissue growth.
2. Immunomodulation: SVF cells can modify the immune response, possibly reducing harmful inflammation that can impede healing.
3. Stimulating Neoangiogenesis: As you mentioned, the SVF cells can promote the formation of new blood vessels. This not only assists in delivering nutrients and oxygen to the healing tissues but also helps in the removal of waste products.
4. Cell Differentiation: Some cells in SVF have the potential to differentiate into various cell types, which can replace damaged cells in the target tissue.
5. Supporting Matrix Remodeling: SVF cells release enzymes and other factors that can help in remodeling the extracellular matrix, which is crucial for tissue repair.
The exact mechanisms and the efficiency of SVF treatments in various medical conditions are still being studied, with research exploring their use in orthopedics, wound healing, and cosmetic procedures, among other fields. Clinical applications are being developed, but their use is subject to regulatory approval and ethical considerations.
What transpires during the procedure?
Initial steps
Before the procedure commences, a thorough evaluation of the patient's health history and symptoms is conducted. Once in the operating room, the patient undergoes a sterilization process and receives either oral or twilight anesthesia, supplemented with a local anesthetic.
Once anesthesia takes effect, a small, rice-sized incision is made in an area abundant with fatty tissue, like the buttocks, abdomen, or flank. Fat tissue is then carefully extracted using a specialized syringe. This fat tissue, now referred to as lipoaspirate, is treated with a collagenase solution to break down the extracellular matrix and release cells from the fat tissue. Subsequently, this mixture is centrifuged to isolate the stromal vascular fraction (SVF). The SVF solution is then administered to the patient. Post-procedure, the patient may be observed for a period of time depending on the specifics of the clinical procedure.
Fundamental distinction between multipotent MSCs and SVF:
Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are highly researched and form a significant component of the stromal vascular fraction (SVF). These MSCs can transform into a variety of cell types, such as bone, cartilage, muscle, and fat cells. Adipose tissue is particularly abundant in MSCs, yet they require careful laboratory cultivation under sterile conditions to be prepared for clinical applications. In contrast, SVF can be obtained and used shortly after liposuction without the need for such cultivation. SVF not only shares the properties of MSCs but also contains additional stem cell types and bioactive molecules, contributing to its therapeutic effects.
Therapeutic benefits of MSC’s:
Multipotent MSCs offer therapeutic benefits by secreting active molecules like cytokines and growth factors, which assist in regenerative processes including new blood vessel and nerve growth, inflammation modulation, inhibition of cell death, recruitment of stem cells to damaged areas, and promotion of stem cell differentiation.
Safety Profile of SVF:
Incidence of Risks and Side Effects
Results from clinical trials have demonstrated that local administration of SVF is generally safe, presenting no cases of tumor development, inappropriate tissue growth, or negative reactions. Most patients typically endure the procedure with ease. Instances of individual intolerance are exceptionally infrequent, though they cannot be entirely ruled out. At Total Spine, our experts will oversee your treatment to enhance safety and efficacy, taking necessary precautions to reduce any potential hazards.
Tracking Outcomes:
We are proud to be part of Cell Surgical Network, a global network of highly specialized physicians. Every member of the CSN utilizes the Regenatrak Database to monitor their patients' health outcomes specific to their condition for five years post-treatment. This data is gathered and examined to assist CSN physicians in making optimal decisions regarding personal cell therapy.
The information collected has led to the creation of many leading peer-reviewed articles in the field, accessible at the provided link.