Herniated Discs
If you’ve been diagnosed with a herniated disc, you’re likely familiar with the associated pain and discomfort.
As you explore treatment options for relief, it’s crucial to understand what causes a herniated disc in the first place.
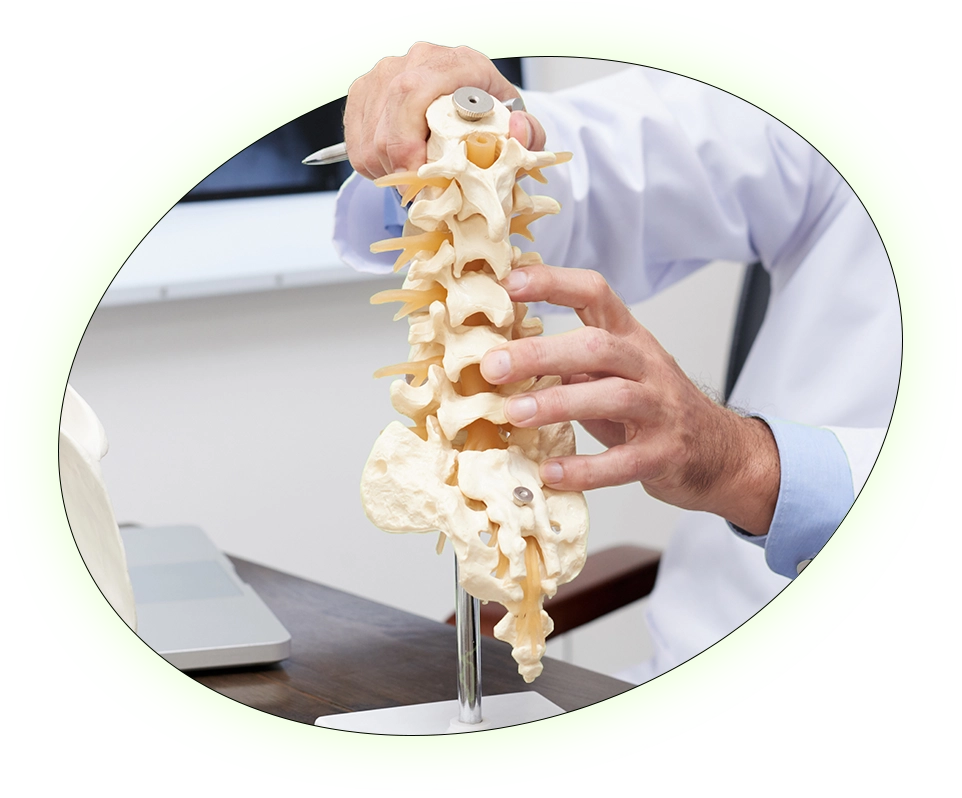
A herniated disc, also known as a disc herniation, ruptured disc, or torn disc, occurs when the inner core of a spinal disc pushes through a tear in its outer layer. Understanding the underlying causes can help determine the most effective treatment plan. For instance, a herniated disc resulting from gradual weight gain might require a different approach than one caused suddenly by an auto accident.
Discs act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae, facilitating movement and reducing friction. Each disc consists of two parts:
Annulus Fibrosus: The tough, collagen-rich outer layer.
Nucleus Pulposus: The gel-like inner core.
These components are high in water content and must remain hydrated to function properly. Over time, discs can dehydrate and deteriorate, becoming brittle and prone to damage. If a fissure develops in the annulus fibrosus, the nucleus pulposus can protrude through, leading to a herniated disc. Pain and other symptoms arise if the displaced material irritates or compresses nearby nerves or the spinal cord.
The spinal column extends from the base of the skull through the cervical spine in the neck, the thoracic spine in the middle back, and into the lumbar spine in the lower back. Comprising 24 individual vertebrae and several fused vertebrae in the pelvic region, the spine is both flexible and strong, allowing a full range of motion while supporting the upper body’s weight.
Several factors can contribute to the development of a herniated disc:

Natural wear and tear weaken discs over time, making them more susceptible to rupture.

Injuries from forceful impacts can cause immediate disc herniation and severe nerve compression.

Prolonged sitting or repetitive heavy lifting can cause small tears in the disc’s outer wall.

Extra body weight, especially around the abdomen, adds strain to the spine.

An unbalanced diet can lead to weight gain and deprive discs of essential nutrients.

Smoking impedes circulation and nutrient delivery, affecting disc health.
While some herniated discs cause no symptoms, others can lead to:

Near the affected disc due to irritation of small nerves.

Nerve compression can impact mobility.

Compression of nerves can affect muscle strength and sensation.

If the herniation compresses spinal nerves, pain can travel through the arms or legs.
A herniated disc can occur in the cervical (neck), thoracic (mid-back), or lumbar (lower back) regions, with symptoms varying accordingly:
If you’re interseted in exploring regenerative medicine for your herniated disc, we’re here to help. Our team of specialists can provide personalized advice and discuss available treatment options.
Various treatments can help manage herniated disc symptoms:

Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs.

Exercises to strengthen the spine and improve flexibility.

Injections to reduce inflammation.

Innovative and natural treatment options to relieve pain.

Procedures to remove or repair the damaged disc.
Here are some of the questions that we are asked most frequently at Total Spine and Wellness
Regenerative medicine aims to replace damaged tissue or organs caused by factors like age, disease, trauma, or congenital issues, as opposed to focusing solely on symptom management. This is achieved through the use of tissue engineering, cellular therapies, medical devices, and artificial organs.
By combining these approaches, we can enhance our body’s natural healing process where it is most needed. Regenerative medicine brings together experts from various specialties who wish to be on the cutting edge of medicine.
When our bodies are injured or affected by disease, they possess an innate ability to heal and defend themselves. What if we could harness this inherent power and accelerate the healing process in a clinically relevant manner? What if we could aid the body in healing more effectively?
The promising field of regenerative medicine strives to restore the structure and function of damaged tissues and organs. It also aims to develop solutions for organs that have sustained permanent damage. Ultimately, the goal of regenerative medicine is to create transformative healthcare solutions that could potentially help injuries and diseases that were previously deemed untreatable.
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells in our bodies that have the remarkable ability to develop into various types of specialized cells. They can divide and renew themselves to form more stem cells or differentiate into specific cell types, such as muscle, nerve, or blood cells. Stem cells play a crucial role in the development, growth, and repair of tissues and organs in our bodies. They hold great potential for medical research and regenerative medicine, as they may be used to treat a wide range of diseases and injuries.
Stem cells have the remarkable ability to develop into different cell types in the body and can also repair damaged tissues. When introduced into a specific area, they can promote healing through various mechanisms. Stem cells can differentiate into the desired cell type, replacing damaged cells directly. They can also secrete growth factors and proteins that stimulate the surrounding cells to regenerate and repair themselves. Additionally, stem cells can modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation, creating a more favorable environment for healing. These combined effects make stem cells a valuable tool for treating degenerative conditions.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a promising source for the treatment of OA due to their multipotency for differentiation into chondrocytes and their ability to modulate the immune system.
These surgical procedures are considered part of a physician’s practice of medicine, allowing both the physician and patient to freely consider their preferred treatment options. While the FDA does provide guidelines for the treatment and manipulation of a patient’s own tissues, Total Spine adheres to these guidelines by offering same-day treatment using the patient’s unaltered cells, which are inserted during the procedure.
Not everyone is a good candidate for stem cell treatment. We offer a complimentary consultation and imaging review to determine if someone is likely to benefit from our treatments. If the severity of the condition is too great and a successful outcome is not likely, the patient will be told that in consultation.
We are a team of highly specialized spine surgeons dedicated to pioneering the future of spine care.